Video, text and code together to learn how to implement LTI 1.3 advantage
This is a personal project to help developers bootup on LTI 1.3 Advantage. Make sure to check-out IMS Global official page with the actual specifications and additional resources on imsglobal.org. LTI is a trademark of IMS Global.
LTI 1.3 is out! In many ways it could have been called LTI 13. In apparence it still delivers the LTI experience you are familiar with, underneath, the technology has radically changed to embrace modern web practices and build a strong secure foundation for the LTI ecosystem to grow on.
LTI Bootcamp
This bootcamp is made of:
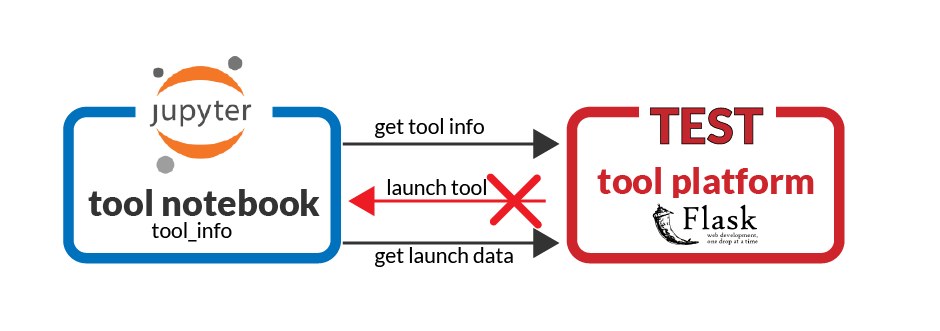
- Jupyter Notebook: to simulate a Tool interacting with a learning platform
- Flask Server: an LTI platform simulator, implementing most of LTI 1.3 Advantage, called from the notebook
By blending text with code that one can actually run and tamper with, Jupyter Notebook offers a great way to do active learning.
The Notebook guides you through the steps of building a tool interacting with a learning platform, from registration to LTI launches, deep linking and grade exchange.
You can have a read-only idea of the notebook directly in github: notebook but it’s way better to actually run it :) For that, see below…
Youtube videos
Alongside the development of the notebook, there are a set of hand-drawn videos explaining LTI 1.3 and Advantage (WIP):
Limitation of the bootcamp
The bootcamp uses Notebook to mix live code and text. Since the platform cannot launch into Jupyter, the bootcamp LTI server has API to get launch data (the data a tool would normally receive in the launch POST request); the notebook is not launched for the platform; rather the notebook asks for the launch data.
How to use
Once you have the notebook and the server up, open the ltibootcamp notebook, and enter the server URL where asked for. Then follow the book…
Docker
docker run -p 5000:5000 -p 8888:8888 -t claudevervoort/ltibootcamp:latest
Or build the latest locally:
docker build . -t ltibootcamp
docker run -p 5000:5000 -p 8888:8888 -t ltibootcamp
Or use Docker Compose:
docker-compose up -d
Hosted version
There is a hosted version running on a tiny OVH server, it might be up and ready for you to try!
- go to https://notebook.theedtech.dev
- login: any username, and the magic word is ltib00t!
- the learning platform url to use is: https://ltiplatform.theedtech.dev
Virtual Env
With Python3 around, you can easily run the bootcamp:
You can run the jupyter notebook and the lti server in 2 virtual envs. See Jupyter README and Server README.
The server URL is going to be: http://localhost:5000 . Verify it runs. Jupyter should have opened in your browser, so just need to navigate to the notebook.